Constraint Relations
Constraint Relations: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Constraint Equations, String Constraint, Wedge Constraint, Constraint Equation in Inclined Planes, Constraint Equation in Wedges, Motion of Connected Bodies, and Motion on Inclined Plane.
Important Questions on Constraint Relations
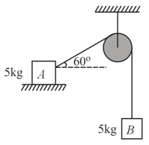
The coefficient of static friction, , between block of mass and the table as shown in the figure is . What would be the maximum mass value of block so that, the two blocks do not move? The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless .
A block has been placed on an inclined plane with the slope angle block slides down the plane at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is equal to :
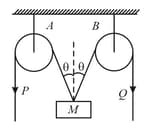
In the arrangement shown in the figure, the points and of the two inextensible strings move downwards with uniform speed . If the pulleys and are fixed, then the mass moves upwards with a speed
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (vertically). If the acceleration of the system is , then the ratio of the masses is –
Two masses and tied to a string are hanging over a light frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses when left free to move? ( )
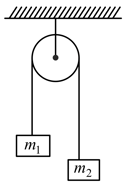
Two masses and tied to a string are hanging over a light frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses when left free to move? ( )
A particle starts sliding down a frictionless inclined plane. If is the distance travelled by it from time to , the ratio is
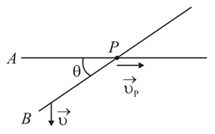
Two infinitely long rods are arranged on a plane making an angle with each other, as shown in the figure. The rod B starts to move with a uniform velocity in a direction perpendicular to rod Thus, the point of intersection moves with a horizontal velocity Which of the following statements is true ?
A block of mass is pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by a rope of mass . If a force is applied at the free end of the rope, the force exerted by the rope on the block is
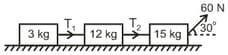
Three masses are connected as shown in the figure, are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface and pulled by a force of . The tensions and are in the ratio:
A monkey of mass 40 Kg climbs on a massless rope which can stand a maximum tension of . In which of the following cases will the rope breaks? (Take )

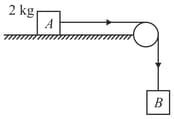
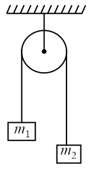
A block of mass placed on a frictionless horizontal table is pulled by an other block of mass hanging vertically by a massless string passing over a frictionless pulley. The tension in the string is
As shown in the figure, two particles, each of mass tied at the ends of a light string of length are kept on a frictionless horizontal surface. When the mid point of the string is pulled vertically upwards with a small but constant force the particles move towards each other on the surface. Magnitude of acceleration of each particle, when the separation between them becomes is
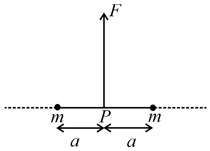
A block of mass resting on a wedge of angle as shown in the figure. The wedge is given an acceleration a towards left. What is the minimum value of a due to external agent so that the mass falls freely ?
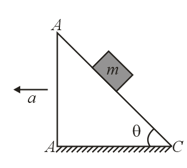
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (vertically). If the acceleration of the system is then the ratio of the masses is :
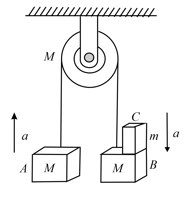
Two masses of and respectively are connected by a massless spring as shown in the below figure. A force of acts on the mass. At the instant shown the mass has acceleration . What is the acceleration of mass ?
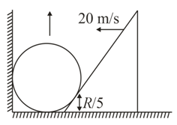
A sphere of radius is in contact with a wedge. The point of contact is from the ground as shown in the figure. Wedge is moving with velocity then the velocity of the sphere at this instant will be:
Three identical ballsare suspended on springs one below the other as shown in the figure. is a weightless thread. The balls are in equilibrium
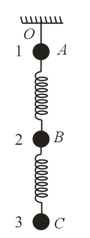
If the thread is cut, the system starts falling. Find the acceleration of all the balls at the initial instant